I Type Fin Tube|Tension Wound Finned Tube
The fin strip is tension wound onto the base tube. Typical fin materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, brass and copper-nickel
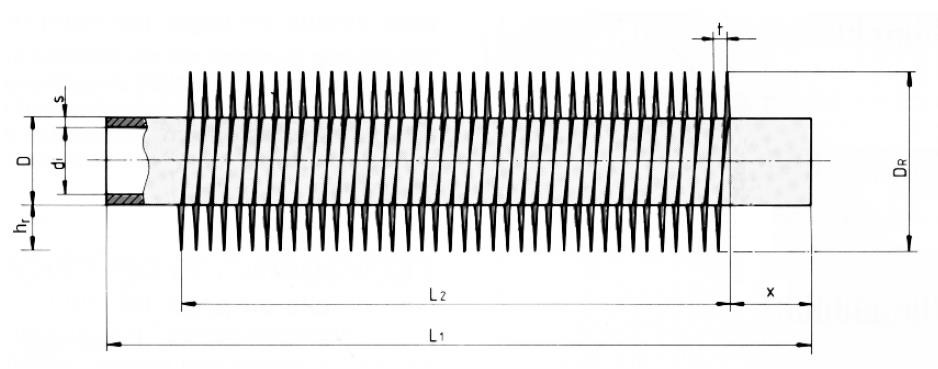
 I Type Fin Tube Size Range:
I Type Fin Tube Size Range:
Base tube size: 6-219.1 (other sizes upon request)
Fins: 50-500 fins/meter
Fin thickness: 0.2-1.5 mm
Fin quantity and size depend on diameter of base tube. In case of deviation against the sizes of the opposite page, please ask us.
Tolerances: Fin height: +/- 1mm
Fins/meter: +/- 2%
Plain ends: +/- 5mm
I Type Fin Tube Fields of Application:
Climatic Industry, Cooling, Heating, Drying
I Type Fin Tube Manufacturing Process
For I type fin tube, the fins are spirally wound on a base tube, without welding, just fin spot welded. Non ferrous tubes and fins on either
root soldered or completely tinned
Execution: black, galvanized and for special applications
Stainless Steel, Copper, Brass, and/or Aluminium.
Ends can be bevelled, bended upon request.
In order to forward you a promt offer we would be pleased to receive you detailed enquiry containing:
• Base tube material and quantity
• Base tube size
• Fin material
• Fin type
• Fin diameter or height
• Fin thickness
• Fins per inch, meter or fin pitch
• Lenght of plain, unfinned ends (nessesary to roll or weld the tubes into tubeplate or assembly)
Comments
Post a Comment